Serial Output
Gocator's web interface can be used to select measurements to be transmitted via RS-485 serial output. Each sensor has one serial output channel.
Two protocols are supported: ASCII Protocol and Selcom Serial Protocol.

|
Gocator 2500 series sensors do not support the Selcom serial protocol. |

|
Gocator 2600 series sensors do not support the Selcom serial protocol. |
The ASCII protocol outputs data asynchronously using a single serial port. For information on the ASCII Protocol parameters and data formats, see ASCII Protocol.
The Selcom Serial Protocol outputs synchronized serial data using two serial ports. For information on the Selcom serial protocol and data formats, see Selcom Protocol.
For information on wiring serial output to an external device, see Serial Output.
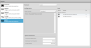
To configure ASCII output:
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Select Standard to use the default result format of the ASCII protocol. Select value and decision to send by placing a check in the corresponding check box. See Standard Result Format for an explanation of the standard result mode. Select Custom to customize the output result. A data format box will appear in which you can type the format string. See Custom Result Format for the supported format string syntax. |
|||
Select measurements by placing a check in the corresponding check box. |
|||
Select the delimiter, termination and invalid value characters. Special characters are used in commands and standard-format data results. |
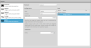
To configure Selcom output:
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
To select an item for transmission, place a check in the corresponding check box. Measurements shown here correspond to measurements that have been programmed using the Measurements page. |
|||
|
|||
See Selcom Protocol for definitions of the formats. |
|||
The Data Scale values are specified in millimeters for dimensional measurements such as distance, square millimeters for areas, cubic millimeters for volumes, and degrees for angle results. The results are scaled according to the number of serial bits used to cover the data scale range. For example, the 12-bit output would break a 200 mm data scale range into 4096 increments (0.0488 mm/bit), and the 14-bit output would break a 200 mm data scale range into 16384 increments (0.0122 mm/bit). |
|||
The scheduled delay must be longer than the processing latency to prevent drops. |