Triggers
A trigger is an event that causes a sensor to take a single image. Triggers are configured in the Trigger panel on the Scan page.
When a trigger is processed, the laser is strobed and the camera exposes to produce an image. The resulting image is processed inside the sensor to yield a
The sensor can be triggered by one of the sources described in the table below.

|
If the sensor is connected to a Master 400 or higher, encoder and digital (external) input signals over the IO cordset are ignored. The sensor instead receives these signals from the Master; for encoder and digital input pinouts on Masters, see the section corresponding to your Master in Master Network Controllers. If the sensor is connected to a Master 100 (or no Master is used), the sensor receives signals over the IO cordset. For information on connecting encoder and digital input signals to a sensor in these cases, see Encoder Input and Digital Input, respectively. |
| Trigger Source | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time |
Sensors have an internal clock that can be used to generate fixed-frequency triggers. The external input can be used to enable or disable the time triggers. |
||
| Encoder |
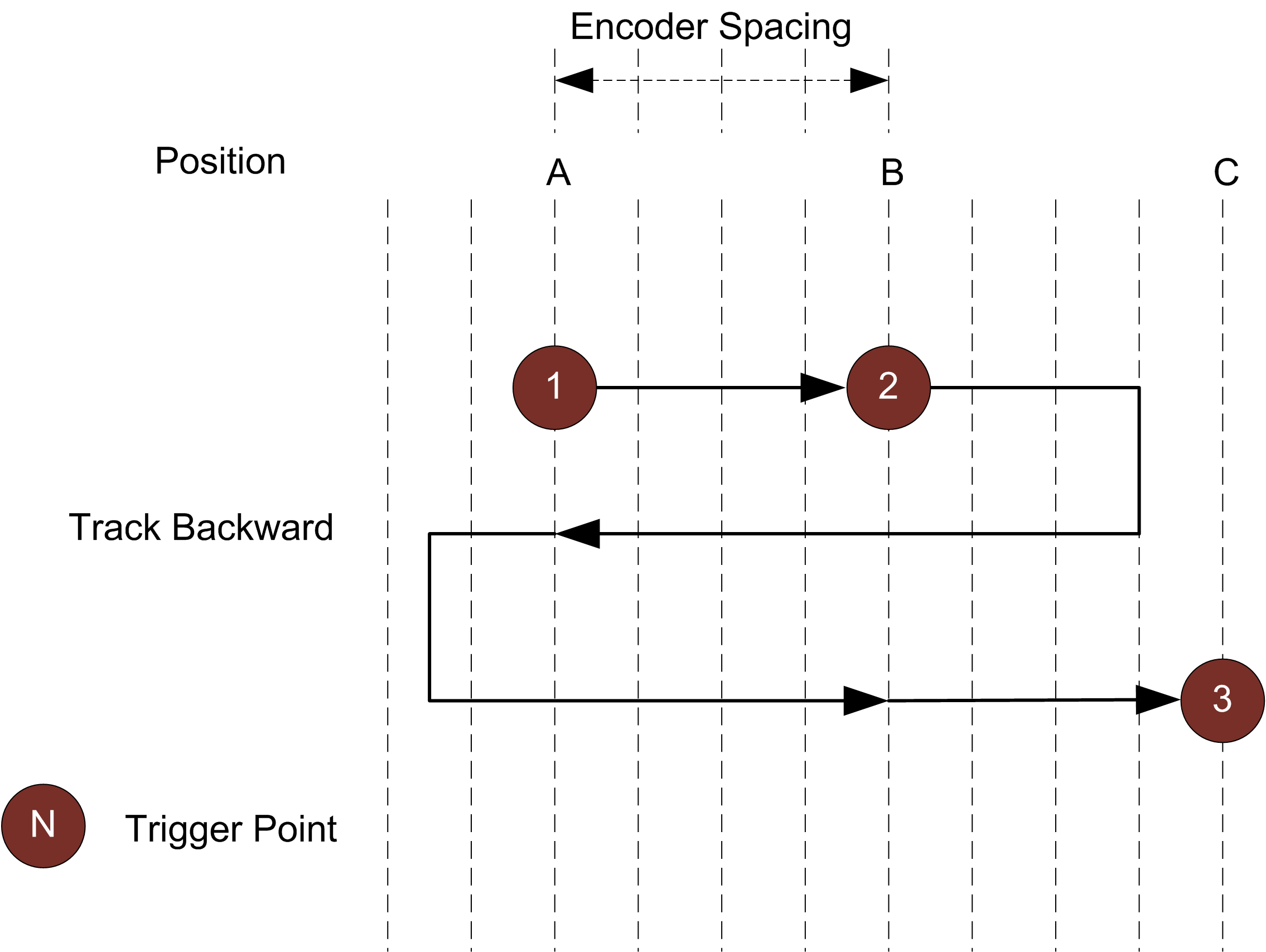
An encoder can be connected to provide triggers in response to motion. Three encoder triggering behaviors are supported. These behaviors are set using the Behavior setting. Track Backward A scan is triggered when the target object moves forward. If the target object moves backward, it must move forward by at least the distance that the target travelled backward (this distance backward is "tracked"), plus one encoder spacing, to trigger the next scan.
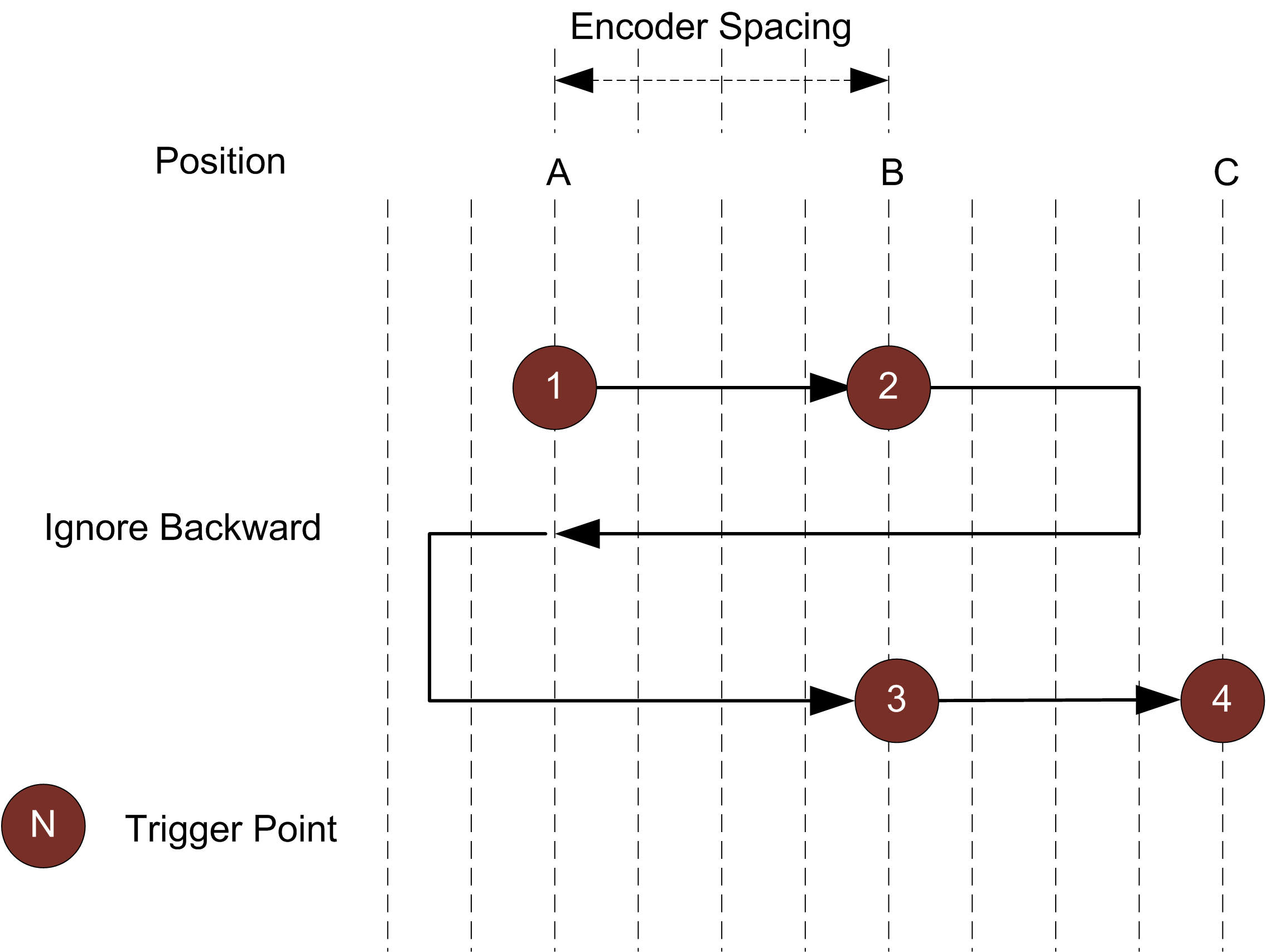
Ignore Backward A scan is triggered only when the target object moves forward. If the target object moves backward, it must move forward by at least the distance of one encoder spacing to trigger the next scan.
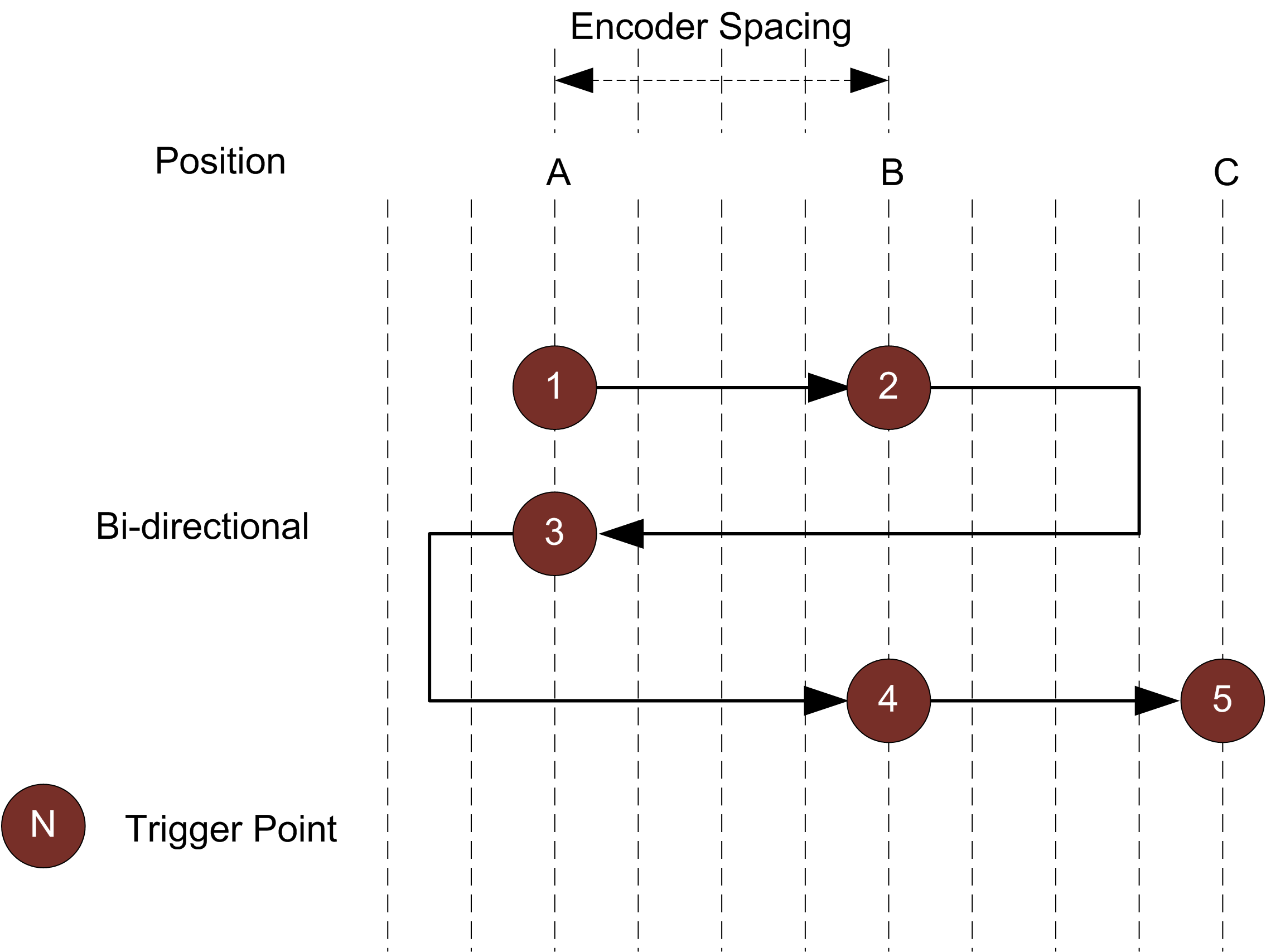
Bi-directional A scan is triggered when the target object moves forward or backward.
When triggers are received at a frequency higher than the maximum frame rate, some triggers may not be accepted. The Trigger Drops Indicator in the Dashboard can be used to check for this condition. The external input can be used to enable or disable the encoder triggers. For information on the maximum encoder rate, see Maximum Encoder Rate.
|
||
| External Input |
A digital input can provide triggers in response to external events (e.g., photocell). The external input triggers on the rising edge of the signal. When triggers are received at a frequency higher than the maximum frame rate, some triggers may not be accepted. The Trigger Drops Indicator in the Dashboard page can be used to check for this condition. For information on the maximum input trigger rate, see Maximum Input Trigger Rate. |
||
| Software |
A network command can be used to send a software trigger. See Protocols for more information. |
For examples of typical real-world scenarios, see Trigger Examples. For information on the settings used with each trigger source, see Trigger Settings.