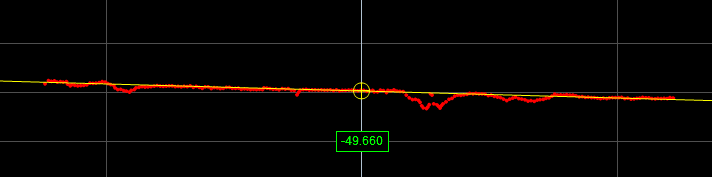
Bridge Value
The Bridge Value tool calculates the "bridge value" and angle of a scanned surface. A bridge value is a single, processed range that is an average of a laser line profile that has been filtered to exclude user-definable portions of highs and lows in the profile. The resulting value represents a "roughness calculation." A bridge value is typically used to measure road roughness, but can be used to measure the roughness of any target.
The tool provides two additional measurements (Window and StdDev) that can help determine whether the scanned data is valid; for more information, see Measurements.

|
The Bridge value tool is only available when Uniform Spacing (in the Scan Mode panel on the Scan page) is unchecked, as the tool only works with unresampled data. For more information, see Uniform Data and Point Cloud Data. |
Understanding the Window and Skip Settings
The Bridge Value tool measurements work on a histogram of the ranges that make up the profile. The Window and Skip parameters together determine what segment of the heights in the histogram is used to calculate the bridge value. The following diagram illustrates the portion of the points of a histogram that would be included for calculating the bridge value, where Window is roughly 85% of the total points of the histogram, and Skip is roughly 15% of the points.

Profile point heights in the white area are included in the calculation of the average. Profile point heights in the grey area are excluded. By adjusting the Window and Skip parameters, you can exclude profile point heights that correspond to unwanted features on the target. In road roughness applications, for example, you could exclude rocks (profile points higher than the road surface), cracks or tining valleys (profile points lower than the road surface), and so on, to get an accurate representation of the tire-to-road interface.
For more information on parameters, see the Parameters table below.
|
|
|
For information on adding, managing, and removing tools and measurements, as well as detailed descriptions of settings common to most tools, see Tools Panel.
Measurements and Settings
| Measurement | Illustration |
|---|---|
|
Bridge Value Determines the bridge value of the profile. |
|
|
Angle Determines the angle of the line fitted to the profile. When Normalize Tilt is unchecked, the measurement always returns 0. |
|
|
Window Returns the height of the area on the profile resulting from the Window and Skip settings. If you are using this measurement on a Gocator 2342 sensor, see Using Window and StdDev as Metrics Measurements for more information. |
|
|
StdDev Returns the standard deviation of the data in the area on the profile resulting from the Window and Skip settings. If you are using this measurement on a Gocator 2342 sensor, see Using Window and StdDev as Metrics Measurements for more information. |
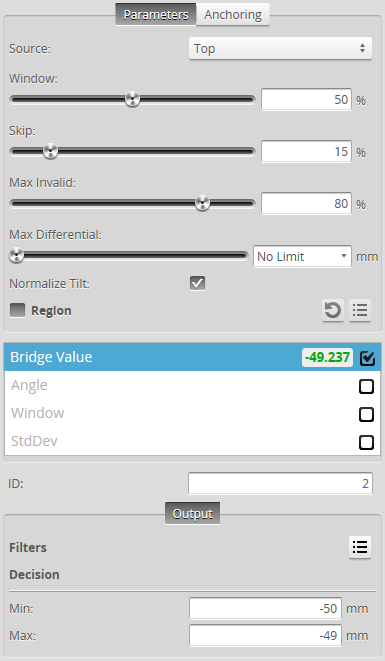
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Source |
The sensor |
|
Stream |
The data that the tool will apply measurements to. This setting is only displayed when data from another tool is available as input for this tool. |
|
Window |
A percentage of the profile point heights in the histogram, starting from the highest point, to include in the average. For example, a setting of 50% would include the highest 50% of the heights. The Skip parameter then determines the actual portion of the profile point heights used to calculate the average. The Window setting in effect sets the lower limit of the profile point heights in the histogram to be used in the average. Use the setting to exclude lower parts of a profile that you do not want to include in the measurement. |
|
Skip |
A percentage of the profile point heights in the histogram, starting from the highest points, to exclude from the average. The Skip setting basically sets the upper limit of the profile point heights in the histogram to be used in the average. Use the setting to exclude higher parts of a profile that you do not want to include in the measurement. If Skip is greater than Window, an invalid value is returned. |
|
Max Invalid |
The maximum percentage of invalid points allowed before an invalid result is returned. |
|
Max Differential |
The maximum difference between the maximum and minimum histogram values before an invalid measurement value is produced. |
| Normalize Tilt |
Fits a line to the profile and shears the points in the Z direction by the angle between the fitted line and the X axis. The Window and Skip settings are applied to the histogram of the transformed data. Useful for surfaces that are tilted. |
|
Region |
The region to which the tool's measurements will apply. For more information, see Regions. |
|
Filters |
The filters that are applied to measurement values before they are output. For more information, see Filters. |
|
Decision |
The Max and Min settings define the range that determines whether the measurement tool sends a pass or fail decision to the output. For more information, see Decisions. |
| Anchor | Description |
|---|---|
|
X or Z |
Lets you choose the X or Z measurement of another tool to use as a positional anchor for this tool. |

|
A measurement must be enabled in the other tool for it to be available as an anchor. The anchor measurement should also be properly configured before using it as an anchor. |

|
For more information on anchoring, see Measurement Anchoring. |
Using Window and StdDev as Metrics Measurements
When a tracking window is defined, if the profile moves too quickly out of the tracking window and there is excessive noise in the scan data (caused for example by ambient light), the tracking window may track the noise instead of switching to search mode to find the actual profile. As a result, the Bridge Value tool receives bad data and returns incorrect or invalid measurements.
On Gocator 2342 sensors, the Bridge Value tool’s Window and StdDev measurements can be used as metrics to determine how valid the Bridge Value measurement is. The Window and StdDev measurements force an enabled tracking window to switch to search mode when either measurement returns a fail decision or an invalid value. The measurements’ Min and Max decision settings should be set to define a range that reflect the expected target roughness so that the tracking window does not switch to search mode: For example, the Window measurement should correspond to the height of the area resulting from excluding highs and lows from the profile with the Window and Skip settings.

|
If the Window or StdDev measurements consistently return fail decisions or invalid measurements, the exposure may be set too high, creating excessive noise. Adjust the exposure to reduce the noise. |